A guide to Wiredcraft's best cybersecurity practices
At Wiredcraft, we prioritize cybersecurity and implement a range of effective strategies to ensure the safety of our clients' information. Here we have clear guidelines that help our team stay on the same page.
Last month, a CrowdStrike update caused a massive Blue Screen of Death issue on Windows systems worldwide, affecting 8.5 million devices and disrupting critical sectors like air travel and banking.
Later, CrowdStrike claimed that this was “not a security incident or cyberattack.” However, as global digitalization accelerates, cybersecurity is becoming increasingly crucial for businesses.
At Wiredcraft, we prioritize cybersecurity and implement a range of effective strategies to ensure the safety of our clients’ information. Here we have clear guidelines that help our team stay on the same page.
Network Security
Manage and control network traffic using security rules at different levels like VPC, Subnet, and Instance.
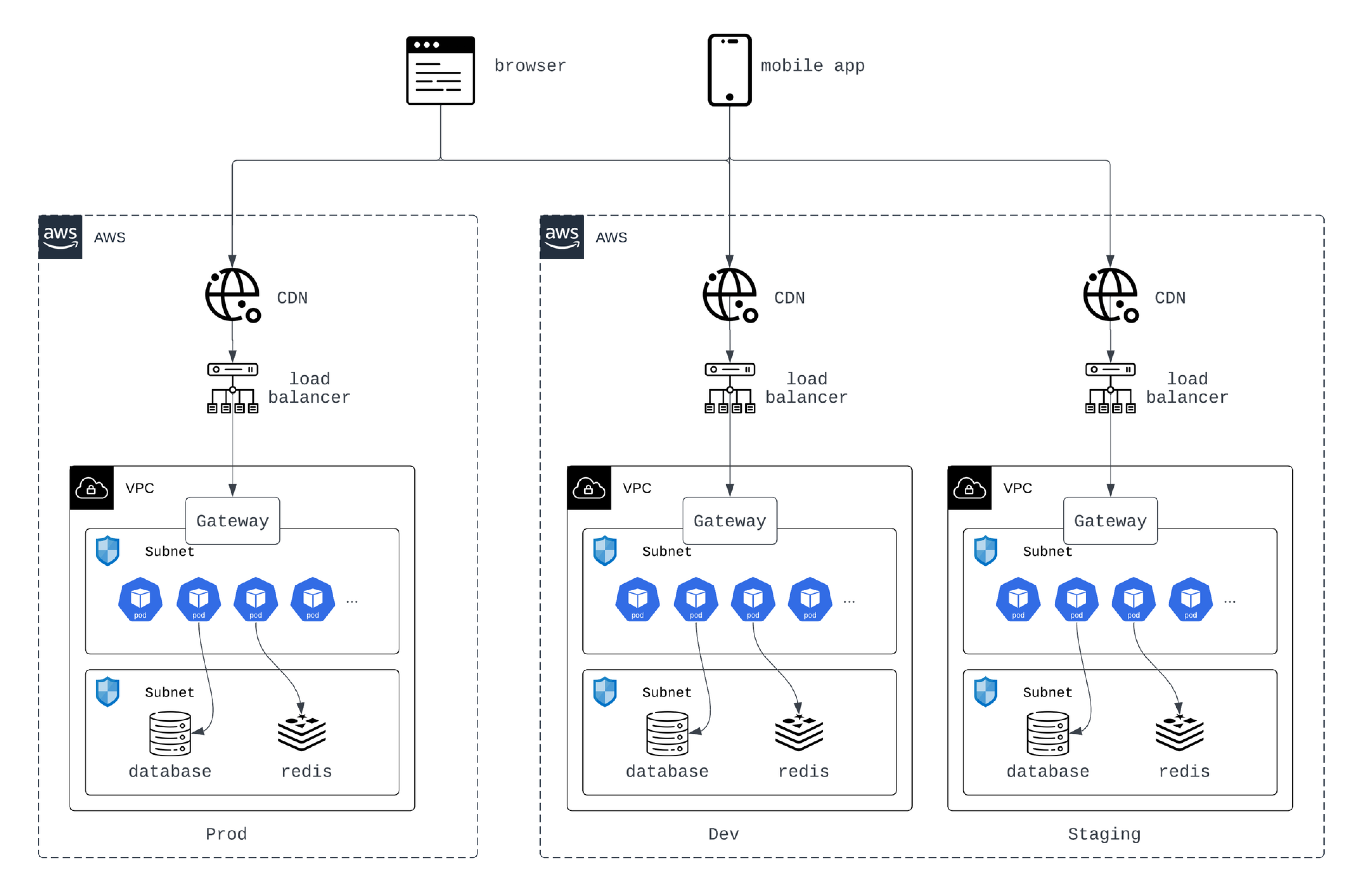
Isolated Environments
Create separate environments for development, staging, and production by isolating them at the VPC level. Each environment has its own network segment to prevent cross-environment issues.
Action:
Dedicated VPCs for each environment
Isolation of Critical Components
Keep critical systems like databases in their own subnets with tightly controlled access to prevent unauthorized entry.
Action: Segregate critical components into restricted subnets
Minimal Exposure
Protect critical components by isolating them at the instance level, limiting access to authorized users only.
Action: Expose only necessary ports (80/443) to the Internet IP whitelisting for critical systems (e.g., admin dashboard) Minimal exposure of protocols (SSH, ICMP, FTP) No root access to servers No password authentication for SSH Monitor and alert on unusual login attempt activities
Host Security
All servers should be updated with the latest security patches and avoid to use EOL (End of Life) software/OS. Also implement proper monitoring and logging to track user activities.
For complex projects, RBAC(Role-based Access Control) is also a MUST.
Action: Update with the latest security patches Session recording to capture all user activities
(We use Teleport at Wiredcraft to manage all the access to our servers.)
Data Security
Protecting data, whether stored or transmitted, is one of the core development concepts at Wiredcraft.
Secrets Management
Securely share sensitive information between teams or individuals. Enable One-Time secret sharing tools( e.g. yopass) for temporary sharing and password management tools(e.g. bitwarden) for persistent sharing.
On the project side, manage confidential data with proven tools (use HashiCorp Vault for big/medium projects and Ansible Vault for smaller projects). Also, make sure to enable secrets scanning in the code build process and Trivy is a useful tool for that.
Action: Enable proper secrets management tools for sharing & sensitive information Integrate secrets management solutions with HashiCorp Vault or Ansible Vault Enable secrets scanning in the code build process
Volume Protection
Use strong encryption methods like AES for local data (disk level) and cloud provider encryption features for remote data (e.g., S3 bucket).
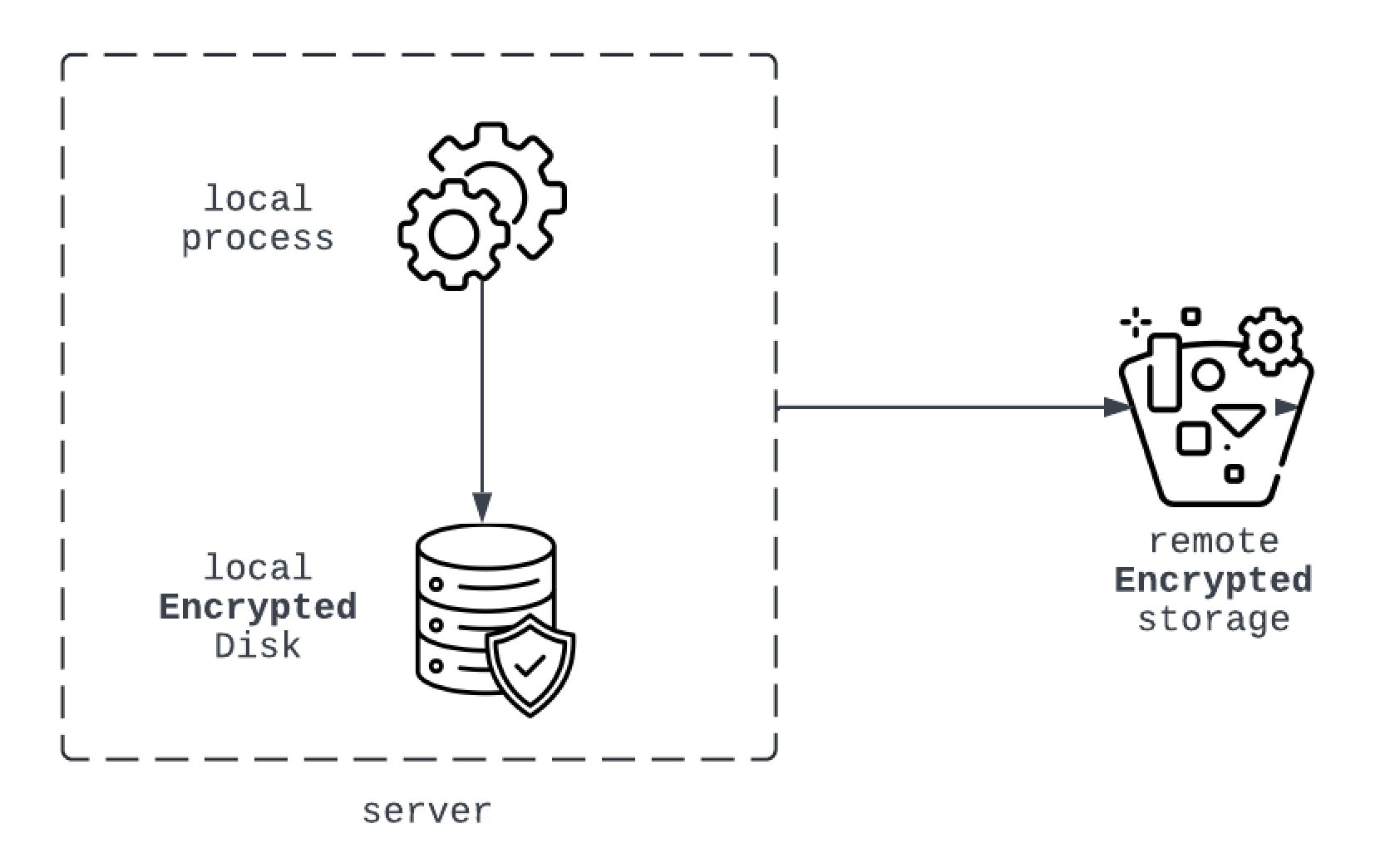
Action: Encrypt all data disks for database servers using AES-256 encryption standards Enable encryption for all data stored in cloud storage services
Data-in-Transit Protection
Use valid SSL/TLS to encrypt data sent across networks. Never use HTTP!
Action: Ensure SSL/TLS is implemented for all web and application servers
Application Security
Manage the requests/vulnerabilities at the application level to prevent unauthorized access and protect against attacks.
Gateway / WAF
Use a gateway(we like Kong) or WAF in front of the application to monitor and block malicious web traffic.
Action: Deploy a Web Application Firewall (WAF) to monitor and block malicious web traffic Implement rate limiting on APIs to prevent abuse and potential denial-of-service attacks Use whitelisting to allow traffic from known, secure sources and blacklist known malicious IPs for important systems
Authentication
Avoid using simple password authentication (like HTTP Basic Auth). Instead, use more secure methods like OAuth2 or OpenID Connect, or API keys/JWT tokens for application integration.
Vulnerability
Regularly scan the application for vulnerabilities and fix them in a timely manner. This includes vulnerabilities in the code, dependencies, and Docker images/OS or any other self-hosted services.
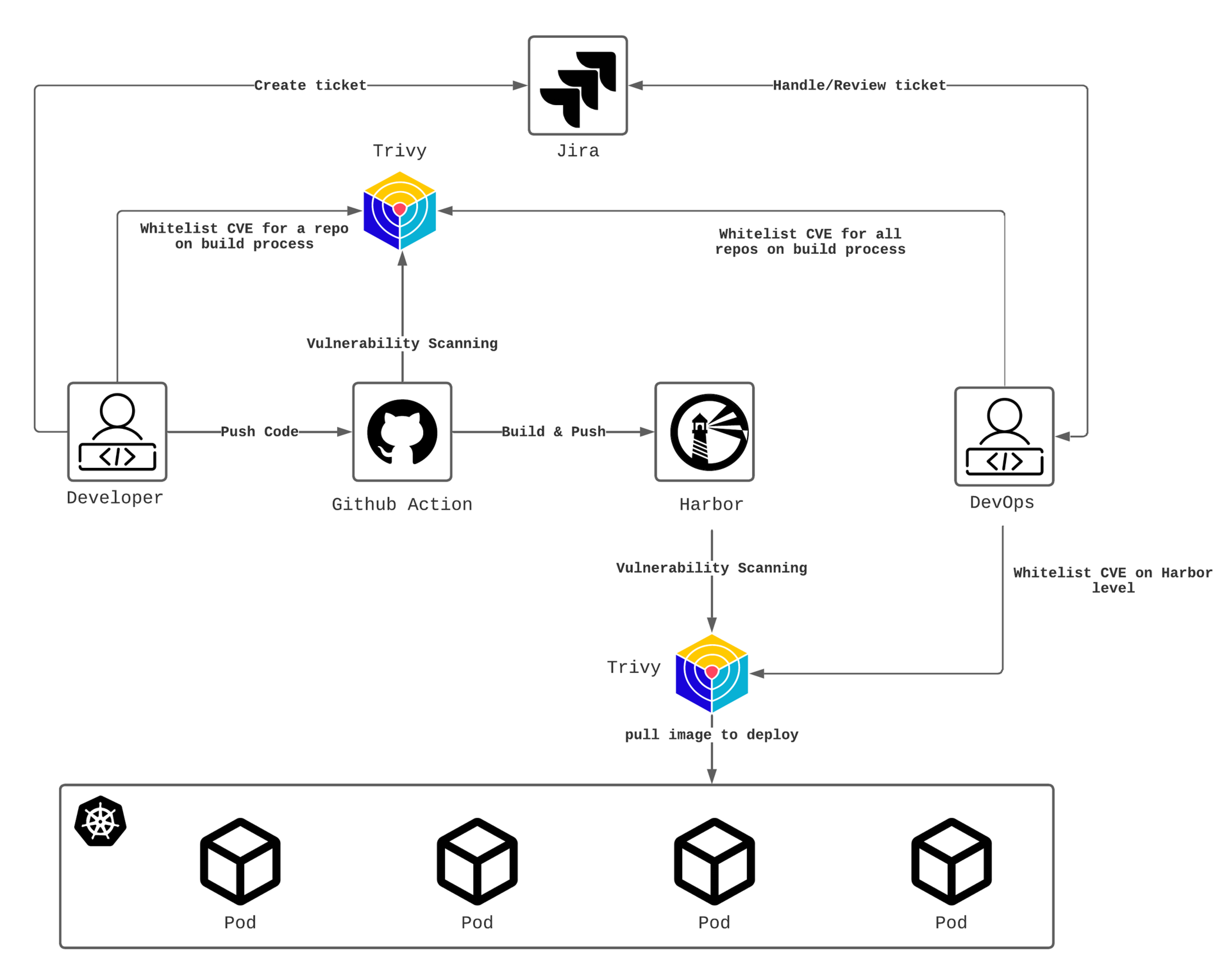
Action:
Integrate vulnerability tool(e.g. Trivy) in the build process to scan all the code Integrate vulnerability tool in registry( e.g. Harbor) to scan all the Docker Regularly check the latest CVEs and update the dependencies Use cloud provider security tools to scan the cloud resources
Pen Testing
For all the critical applications, perform regular pen testing to identify and fix security vulnerabilities before they are exploited by attackers. We use HCL AppScan Standard and BurpSuite and following OWASP Top Ten checklist for security testing.